Almond tree
Prunus amygdalus, Prunus dulcis 
They share to produce a fleshy drupe (commonly called the fruit) coming from the single one carpel, which envelops a stone.
Etymology: the name of the genus Prunus comes from Latin where it indicates the plum tree and amygdalus comes from Greek which indicates the almond.
Origin: Central Asia. From the Vth century before J.C., the almond tree is progressively introduced towards Greece and from there Greeks spread it throughout the rest of southern Europe (in Italy from the IIIth century).
Its introduction in the south of France date back to around 1548. In Spain it was introduced by the Phoenicians, in North Africa by the Arabs.
Habitat: the Almond tree is rather "Mediterranean ". It likes sunny positions, resists well drought (50 - 60 mm of water a month are enough to grow), but it fears spring frosts.
Hardiness: zone 9-10 (it supports cold until -5 °C or 1 °F ).
 Lifespan: more than 100 years (this one was photographed at Antony, close to Paris, France, and is more than 100 years old). The Almond tree is the most lasting fruit tree. But the production exhausts quickly. Lifespan: more than 100 years (this one was photographed at Antony, close to Paris, France, and is more than 100 years old). The Almond tree is the most lasting fruit tree. But the production exhausts quickly.
Shape: broad upright, scattered irregular crown.
Height: 10 m tall.
Often tormented, crooked trunk.
Powerful taproots.
Bark: dark grey and cracked, shedding in small flakes as it matures.
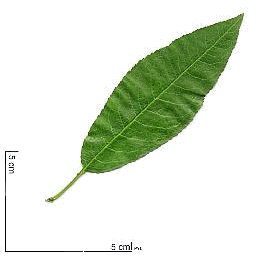
Deciduous, simple leaves, alternate, supported by a short petiole, 7 to 12 cm long, lanceolate and narrow, margin finely toothed. Their color is bright green on the upper surface and grayish on the underside.
Precocious blossoming (February-March). The almond tree is one of the first trees to display its blossoming which delights campaigns (the valley of Ourika, in the south of Morocco!). The flowers of the Almond tree appear before the leaves. They are often grouped by two, attain 5 cm in diameter and have a ruddy calyx and a white or slightly pink corolla. This one has 5 petals and contains many stamens.
Fruit: the fruit is an oval, green and velvety drupe. The fleshy part (the pulpit of the fruit) is not edible. It surrounds a woody shell riddled with holes, hard and brittle, inside which are housed one or more edible seeds, wrapped in a thin coat color cinnamon.
Use: there is sativa variety which produces edible soft almond and amara variety. The soft almond is rich in fatty acids, proteins, calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, vitamins B1, B2 and E. The sweet almond is consumed fresh, dried or paste form, and provides a very fine oil-colored, which is used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Its properties are anti-inflammatory, soothing, emollient, expectorant, moisturizing and toning to treat dry skin and some skin diseases (psoriasis, diaper rash), mouth (sores) or eye.
The bitter almond contains the amygdaloside, causing the grinding of hydrocyanic acid, particularly toxic product, but used in medicine.
Advices of maintenance: for the pruning of fruit trees, see the page.
As most fruit trees, the almond tree is threatened by bacteria, insects and of other diseases: speckle, moniliose, dust mite.
For the treatment, see this page.
Saying: For Sainte-Berthe (July 4th),
Pick the green almond,
If it is full only of milk,
it is necessary to let mature the wheat.
|